Know More About This Test
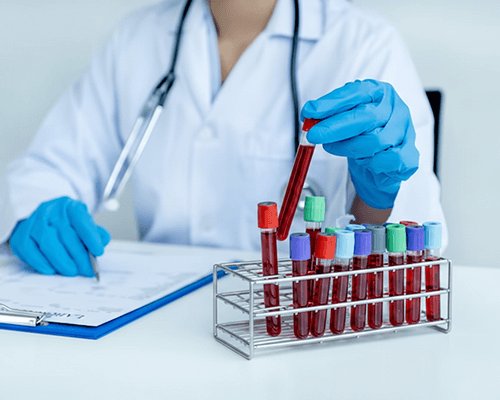
HbA1c measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2–3 months. It reflects how much glucose is bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells and is considered the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring. Unlike fasting or post-meal glucose tests, HbA1c is not influenced by daily fluctuations.
Why Is This Test Recommended?
HbA1c testing is recommended to diagnose diabetes or prediabetes, monitor long-term glucose control in diabetics, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and predict risk of complications such as kidney disease, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease.
What Do the Results Indicate?
Normal levels are <5.7%. Prediabetes is indicated by levels of 5.7–6.4%. Diabetes is diagnosed at ≥6.5%. Higher HbA1c levels indicate poor glycemic control and increased risk of complications such as kidney disease, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease.
How Is the Test Performed and Prepared For?
A blood sample is collected from a vein in your arm. No fasting is required. Continue your routine medications as usual. The test measures glucose bound to hemoglobin over the past 2-3 months.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is HbA1c better than fasting sugar?
Yes for long-term control; HbA1c reflects average glucose levels over 2-3 months, while fasting sugar shows only a single point in time.Can anemia affect results?
Yes; conditions affecting red blood cells like anemia or hemoglobin variants can interfere with HbA1c accuracy and may require alternative testing.Is fasting needed?
No; HbA1c can be tested at any time of day without fasting, making it convenient for routine monitoring.How often should it be tested?
Every 3–6 months; diabetics with stable control may test every 6 months, while those adjusting treatment may need testing every 3 months.Can lifestyle changes reduce HbA1c?
Yes; diet modifications, regular exercise, weight loss, and consistent medication adherence can significantly lower HbA1c levels over time.